How to Configure Microsoft Virtual PC
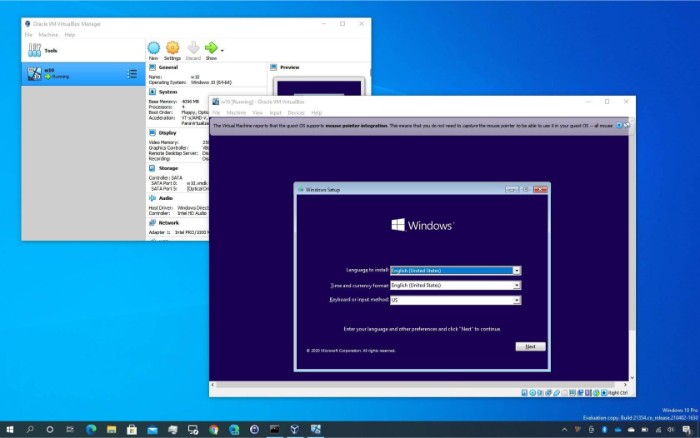
Virtualization technology has transformed the way businesses operate, and Microsoft Virtual PC is one such program allowing users to create and run virtual machines. Users can leverage it for testing software configurations, trying out new operating systems, or setting up a development environment without the need for additional hardware.
Configuring a virtual machine is straightforward. Begin by installing the software on the host machine. Next, choose an operating system, allocate RAM and disk space, and configure network settings. Afterward, install the guest operating system and any necessary applications, just as you would on a physical PC.
An interesting feature of Microsoft Virtual PC is the ability to take snapshots of virtual machines. These snapshots capture the exact state of the machine at a specific point, allowing users to revert if needed. This is excellent for testing new software and making changes without unexpected consequences.
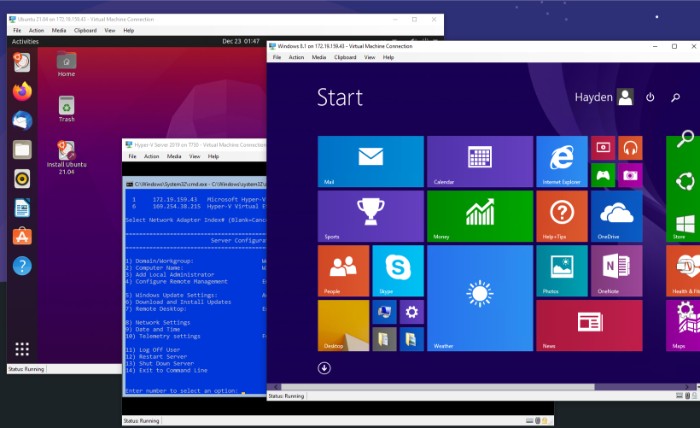 What is Microsoft Virtual PC?
What is Microsoft Virtual PC?
Microsoft Virtual PC is excellent software that enables users to run multiple operating systems on a single physical computer. It utilizes virtualization technology, making it easy and secure to integrate different platforms and run applications.
This technology provides various capabilities for both home and business use. Users can create virtual machines and install Windows, Linux, or previous Windows versions for compatibility testing. It also allows software testing without jeopardizing the stability of the host system.
Moreover, Virtual PC features snapshot functionality, enabling users to save the current state of the virtual machine. This proves valuable for configuration or issue resolution, as users can quickly revert to a working state.
Additionally, Virtual PC supports shared folders between the host and guest operating systems, eliminating the need for complex storage or network setups and facilitating seamless collaboration.
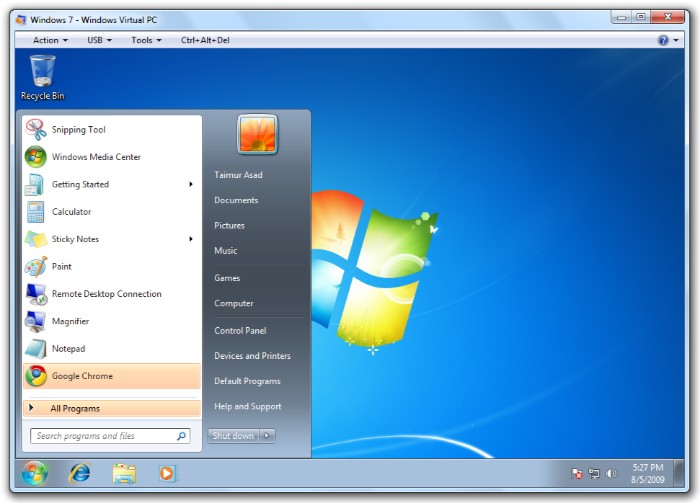 Benefits of Using Microsoft Virtual PC
Benefits of Using Microsoft Virtual PC
Microsoft Virtual PC offers significant advantages for your computer. Here’s why you should consider it:
- Increased Efficiency: Easily switch between operating systems to save time and work more efficiently.
- Cost Savings: Reduce hardware and device costs.
- Enhanced Compatibility: Test software across different environments without risking your main system.
- Simple Maintenance: Create backups and snapshots for quick issue resolution and system restoration.
- Flexibility and Mobility: Carry your virtual environment and transfer virtual machines between computers or devices.
Moreover, Microsoft Virtual PC incorporates advanced security features to protect data and prevent the spread of potential threats.
 System Requirements for Microsoft Virtual PC
System Requirements for Microsoft Virtual PC
Meeting the system requirements is crucial for optimal performance and compatibility when using Microsoft Virtual PC. To enjoy a smooth virtualization experience, users must have a compatible operating system—Windows 7, 8, or 10.
Hardware resources are equally vital. A minimum of 1GB RAM for the host operating system and 512MB for each virtual machine is necessary. Additionally, there should be sufficient disk space for both the host and virtual machines.
For improved performance, the processor should support hardware-assisted virtualization (Intel VT-x or AMD-V).
Understanding and meeting these system requirements during Microsoft Virtual PC setup is essential to ensure a seamless virtualization experience without encountering any issues.
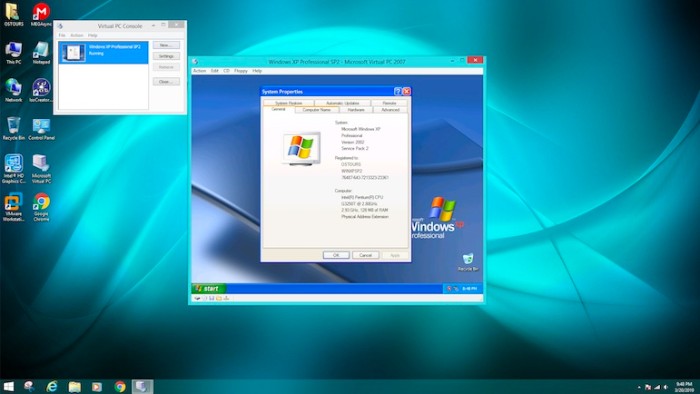 Step 1: Download and Install Microsoft Virtual PC
Step 1: Download and Install Microsoft Virtual PC
Downloading and setting up Microsoft Virtual PC on your computer is crucial for creating virtual machines and running various operating systems. Here’s how to do it:
- Visit the official Microsoft website.
- Locate the download page for Microsoft Virtual PC.
- Click the download link and save the installation file.
- Once the download completes, run the setup file and follow the on-screen instructions.
Successfully installing Microsoft Virtual PC grants access to a powerful tool that can enhance your computer usage experience. With virtual machines, you can simultaneously run multiple operating systems, test software in different settings, or even isolate potentially harmful applications.
Don’t miss the significant opportunity to expand your computing capabilities by configuring Microsoft Virtual PC. Remember, technology advances rapidly, and staying ahead is crucial. Download and install Microsoft Virtual PC now to experience an entirely new realm of possibilities!
Step 2: Configure Virtual Machines
The virtualization world requires configuring virtual machines for smooth operation. Here’s how to do it in Microsoft Virtual PC.
- Launch Microsoft Virtual PC by searching for the Start menu or program files.
- Create a new virtual machine. Choose the operating system and allocate resources such as RAM and disk space.
- Adjust settings for network connectivity, screen resolution, and shared folders.
- Insert the installation media, boot, and follow the operating system installation process.
- Further enhance the virtual machine with provided tools.
- Check the configuration and troubleshoot if necessary.
Understanding the integration of hardware and software, as well as updating MS operating systems for compatibility, is crucial. An interesting fact: MS Virtual PC was developed by Connectix Corp in the ’90s and acquired by MS in 2003. This acquisition significantly influenced the future of virtual machine configurations.
Step 3: Install Guest Operating System
Installing the guest operating system is a crucial step in configuring Microsoft Virtual PC. Launch Virtual PC, select “New,” and pick the operating system from the list.
- Name the virtual machine and choose a storage location.
- Allocate memory for the guest operating system and follow the steps to complete the setup, including disk size and attaching the installation disk or ISO file.
- Ensure valid installation media for the guest operating system, whether it’s a physical disk or ISO file.
- Confirm the virtual machine has sufficient storage space.
Professional Tip: Before installing the guest operating system, take a snapshot of the virtual machine setup. This allows for a quick restoration in case of any issues during or after installation.
Step 4: Configure Virtual Network Settings
Open the virtual machine. Select the desired virtual machine. Click on Settings in the toolbar. In the Settings window, click on the Network tab. Choose a network adapter from the drop-down menu. If your machine needs access to resources on the physical network, select “Shared Networking (NAT).” Otherwise, choose ‘Local Area Connection’ or any other network adapter. This configuration enables safe and seamless communication with other computers/devices on the network. The crucial aspect is choosing the appropriate network adapter based on your needs. Virtual PC provides excellent flexibility for different network setups. It has come a long way since Microsoft introduced it, continuously evolving to meet user needs and preferences.
Step 5: Utilize Microsoft Virtual PC Features
Step 5 allows users to experience the features of Microsoft Virtual PC. Dive deeper into the capabilities.
- Create Virtual Machines: Create multiple virtual machines to test different operating systems and software.
- Manage Snapshot Images: Take some time to capture snapshots. Revert to a previous state if necessary.
- Integrated Tools: Connect the host operating system and virtual machines. Share files and move the mouse/keyboard between them.
- Network Options: Set up networking for your virtual machine. Connect to the physical network or share with other virtual machines.
- USB Support: Use USB devices on your virtual machine. Access storage devices, printers, and other peripherals.
Additionally, make the most of Microsoft Virtual PC. It includes options to optimize resources and customize hardware for each virtual machine.
Professional Tip: Allocate sufficient system resources for each virtual machine to achieve the best performance. Avoid compatibility issues.


