How to resolve error functions in Excel

How to resolve error functions in Excel. Microsoft Excel is popular due to its useful automated calculation features that users can operate with various functions and formulas. However, while using formulas in Excel, encountering errors is unavoidable. In this article, UniTrain will introduce you to some common errors in Excel:
– #DIV/0! Error
– #N/A Error
– #NAME? Error
– #NULL! Error
– #REF Error
1. #DIV/0 Error in Excel
#DIV/0! occurs when working with a formula that divides two values and the divisor (the number being divided by) is zero. It is an abbreviation for dividing by zero error. For example, 90 divided by 0 as shown in the figure below:
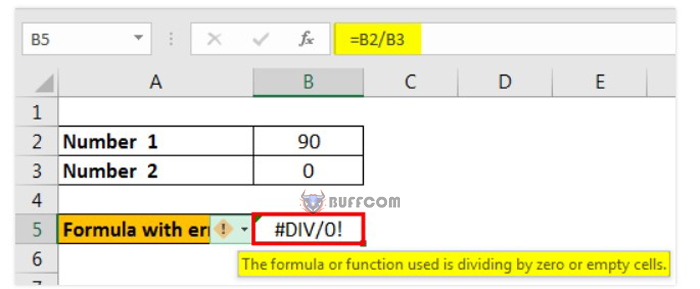
How to resolve error functions in Excel
To resolve this issue, you need to divide by cells with values other than zero. However, when there are empty cells in the worksheet, users can use the IF function as shown below. Use the IF function to avoid #DIV/0 Error by:
Step 1: Assume there is an error as shown in the figure below.
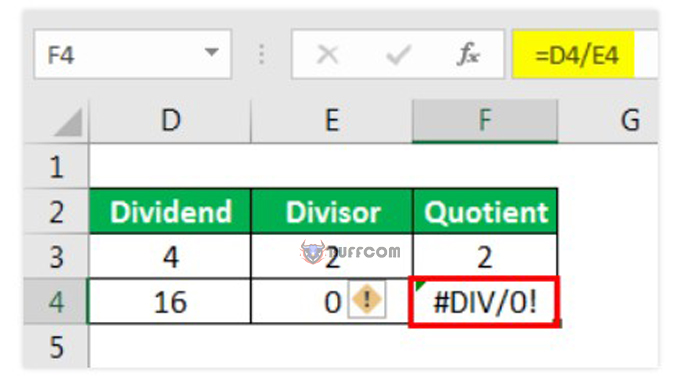
How to resolve error functions in Excel
Step 2: Use the IF function.
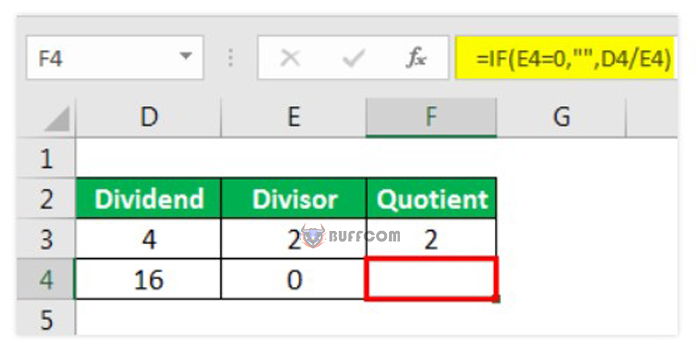
How to resolve error functions in Excel
2. #N/A Error
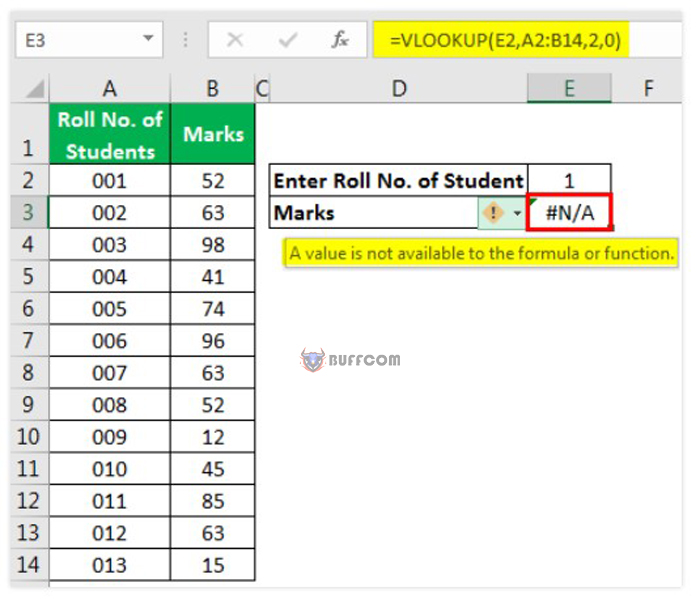
This error means “no value” or “not available”. It indicates that the formula cannot find the value that the user wants it to return. For example, using Excel’s VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, MATCH functions, and LOOKUP function, users may encounter this error if the referenced value is not found in the data source as an argument. Let’s take a look at the example below.
The user has entered “Roll No. of Students” as a number, but the student’s roll number is saved as text in the data source. Therefore, the #N/A error appears.
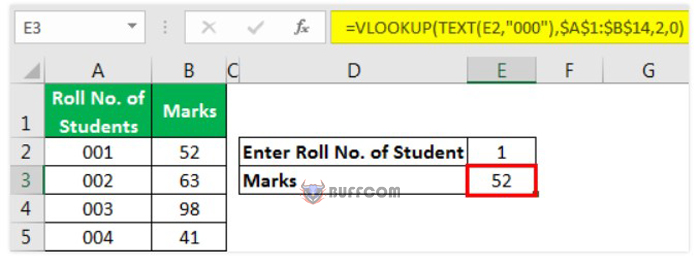
To fix this error, we can either enter the number as text or use the TEXT formula in the VLOOKUP function.
How to resolve error functions in Excel
Users can use the TEXT function in the VLOOKUP function for the lookup_value argument to convert the entered numbers into text.
How to resolve error functions in Excel
How to resolve error functions in Excel
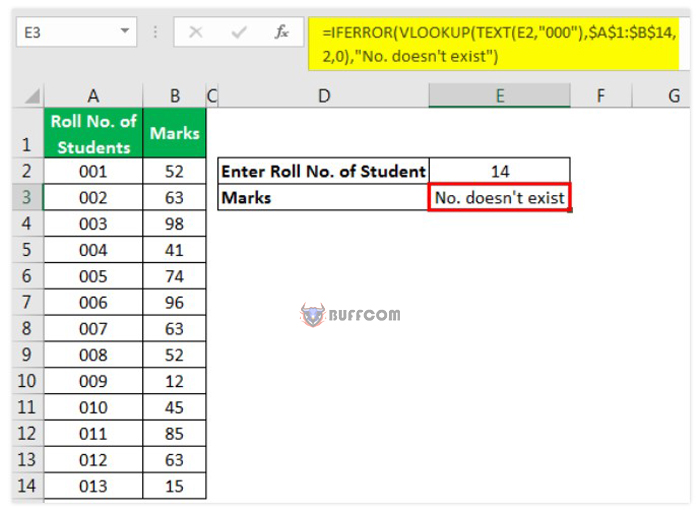
Users can also use the IFERROR function in Excel to display a message if VLOOKUP cannot find the referenced value in the data source.
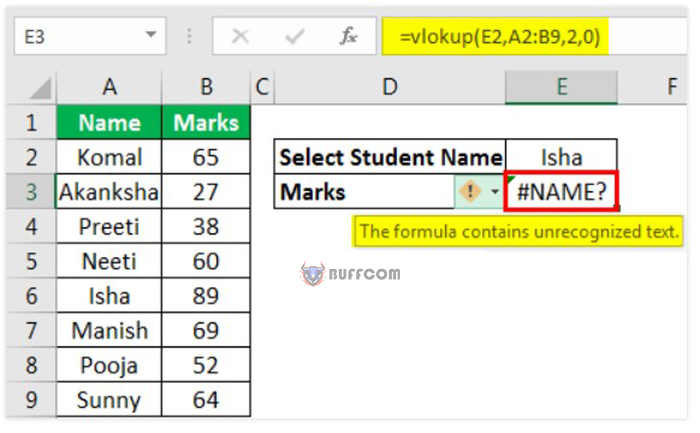
3. #NAME? Error
This error is displayed when the user misspells the function name.
How to resolve error functions in Excel
How to resolve error functions in Excel
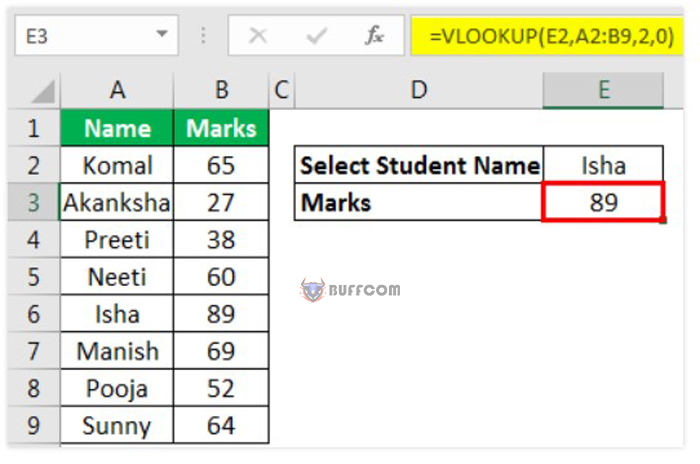
For example, misspelling the VLOOKUP function leads to a #NAME? error in Excel. The only way to fix this error is to enter and check the correct function name.
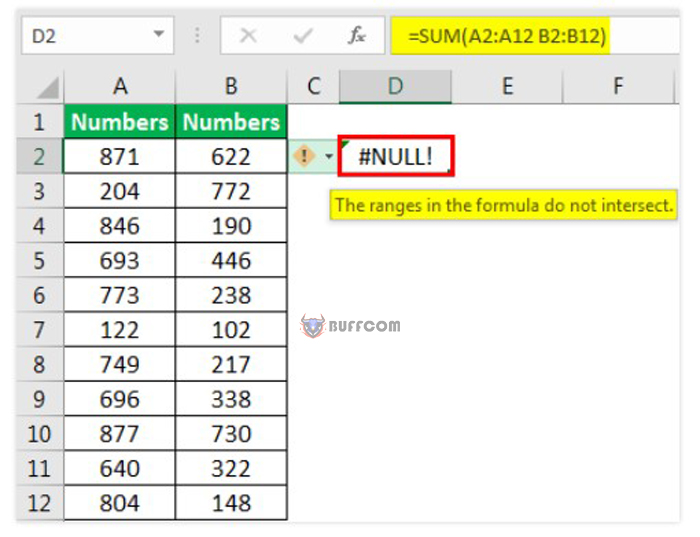
4. #NULL! Error
This error often appears when a cell reference is not specified correctly. Users encounter this error when they do not use white space characters properly. The white space character is called the “intersect operator,” which specifies the intersection range at any cell. In the image below, the user used a white space character, but the ranges A2:A12 and B2:B12 do not intersect, which is why this error is displayed.
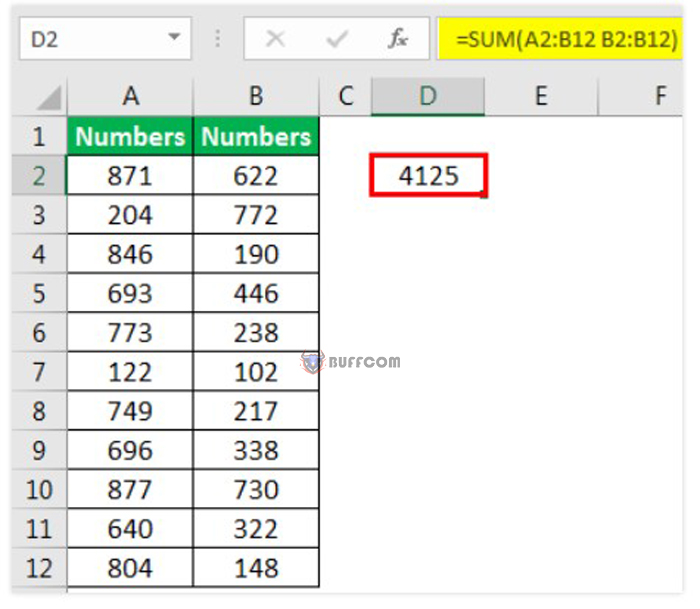
 In the image below, the user can see the sum of the range B2:B12 displayed in cell D2 because, while specifying a range for the SUM function, the user selected two references (with white space), overlapping each other for the range B2:B12. That is why the sum of the range B2:B12 is displayed.
In the image below, the user can see the sum of the range B2:B12 displayed in cell D2 because, while specifying a range for the SUM function, the user selected two references (with white space), overlapping each other for the range B2:B12. That is why the sum of the range B2:B12 is displayed.
 The #NULL! error can also be displayed when using the intersect operator (white space) instead of:
The #NULL! error can also be displayed when using the intersect operator (white space) instead of:
Mathematical Operator (Plus Sign) to calculate the sum.
Range Operator (Colon Sign) to specify the starting and ending cell for a range.
Union Operator (Comma Sign) to separate individual cell references.
5. #REF! Error
This error is an abbreviation for the reference error. This error often occurs when:
– The user accidentally deletes a cell that was referenced in a formula.
– The user cuts and pastes a cell that was referenced to different locations.
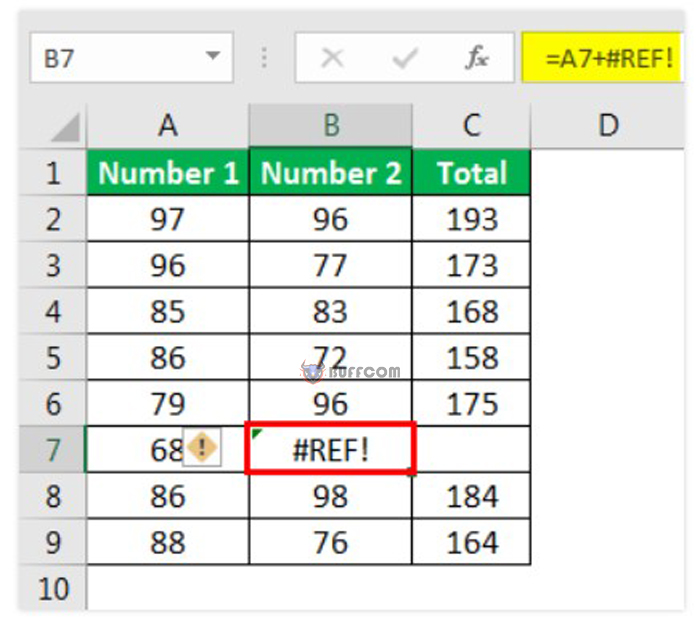 When the user deletes cell B7, cell C7 will shift to the left to replace B7, and the user encounters a reference error in the formula when deleting one of the referenced cells.
When the user deletes cell B7, cell C7 will shift to the left to replace B7, and the user encounters a reference error in the formula when deleting one of the referenced cells.