Security Measures for Windows 7 Professional Environments

Security Measures for Windows 7 marked a significant improvement over Windows Vista, boasting advancements in performance, security, scalability, and user interface. Let’s delve into some key features that set Windows 7 apart.
Security Features: Fortifying the Operating System
Kernel Patch Protection: Windows 7 introduces robust security measures, including Kernel Patch Protection, to safeguard the operating system’s core against unauthorized modifications.
Data Execution Prevention (DEP): DEP enhances security by preventing the execution of code from non-executable memory regions, mitigating potential vulnerabilities.
Enhanced UAC: User Access Control (UAC) underwent improvements in Windows 7, requiring administrator permission for software installations. The modified UAC allows automated actions for non-harmful programs, balancing security and convenience.
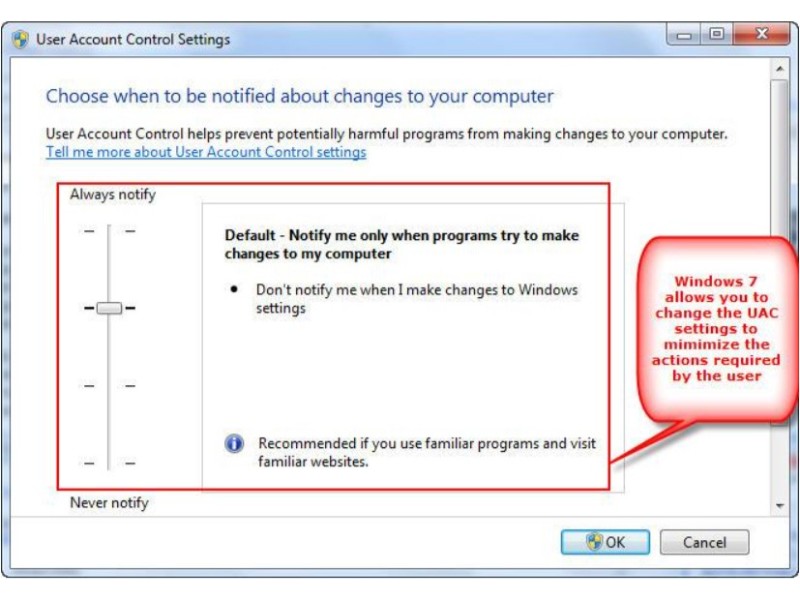
Security Measures for Windows 7
BitLocker: Windows 7 extends BitLocker functionality to external drives, enabling encryption for enhanced data protection. This feature is particularly useful in network environments where sensitive data stored on USB drives needs safeguarding.
Action Center: The Action Center consolidates security and maintenance features, offering a centralized hub to address system issues promptly. It provides notifications in the taskbar, streamlining the resolution of security-related concerns.
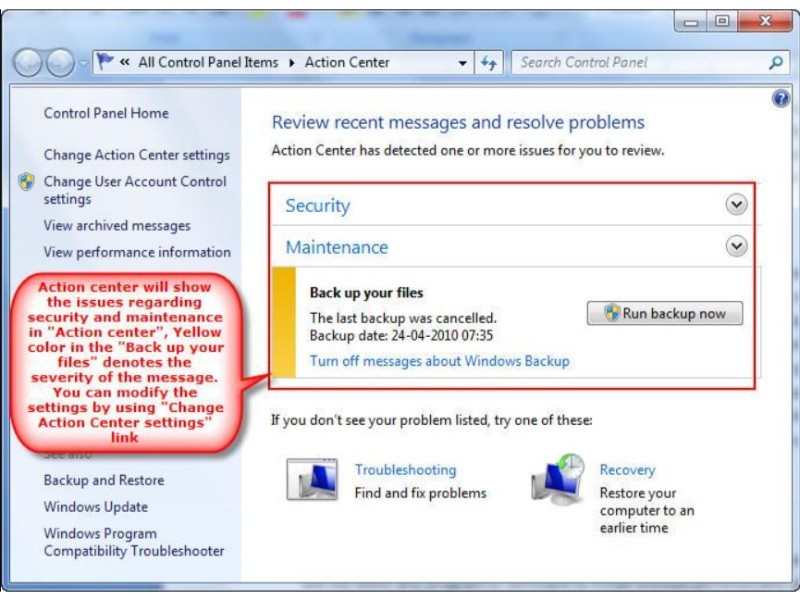
Security Measures for Windows 7
Parental Control: While Windows Vista’s Parental Control focused on internet restrictions, Windows 7 enhances access control. It enables administrators to manage user access based on specific times, restrict program execution, and control gaming activities.
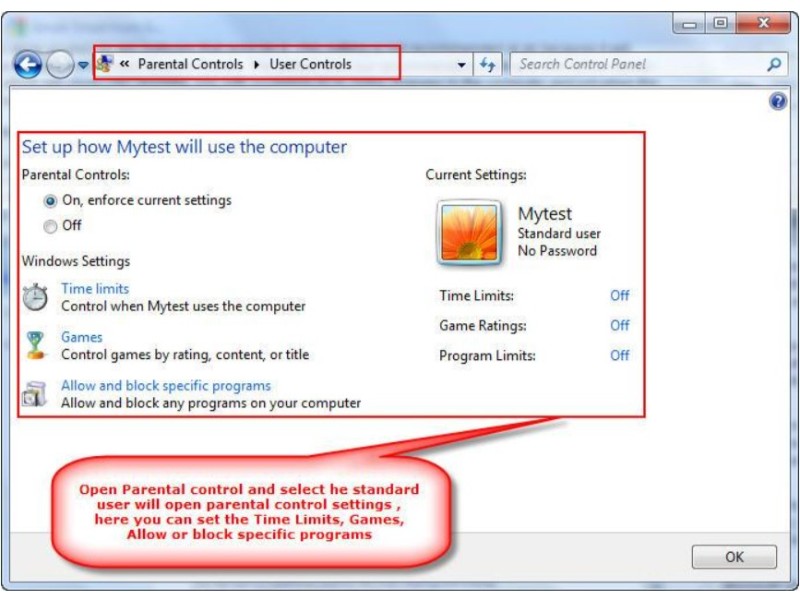
Security Measures for Windows 7
New Features for Improved Functionality:
DirectAccess: Introduced in Windows 7, DirectAccess facilitates secure remote network access without the need for a VPN. It simplifies group policy settings management and enables seamless connectivity to the office network from a remote computer.
Biometric Security: Windows 7 incorporates biometric security, supporting fingerprint readers for user authentication. This method enhances system access security through eye retina, fingerprint, face identification, and DNA recognition.
AppLocker: AppLocker empowers administrators to control the execution of unwanted or unknown software within a network. By setting group policy restrictions, unauthorized software installation is prevented, enhancing network security.
Windows Filtering Platform (WPF): WPF, introduced in Windows Vista, provides APIs for developers to modify firewall, antivirus, and network application settings. It adds an extra layer of security for network-based applications.
PowerShell: Windows PowerShell, a command-line scripting language in Windows 7, aids system administrators in automating tasks. PowerShell scripts offer access to the Windows registry, Remote Desktop Services, and other system components, streamlining administrative functions.
Internet Explorer 8: Bundled with Windows 7, Internet Explorer 8 introduces features like SmartScreen filter for web security, cross-site scripting detection, domain highlighting for safe browsing, and accelerators for quick access to data details.

Security Measures for Windows 7
In conclusion, Windows 7 not only addresses performance concerns but also elevates security measures and introduces user-friendly features, providing a more efficient and secure computing environment.


