Windows Server 2022 enhances over 2019

Windows Server 2022 has ignited a fervent discussion in the tech community, particularly in comparison to its predecessor, Windows Server 2019. Unveiled in August 2021, the decision to migrate to the latest Microsoft Windows Server operating system is not only driven by the usual financial considerations but also by the evolving landscape of remote work and the ever-growing importance of cloud-based storage and management. With an array of new features and a heightened focus on bolstering security, Windows Server 2022 presents a compelling case for organizations to consider an upgrade. Additionally, the imminent cessation of mainstream support for Windows Server 2019 in January 2024 adds urgency to this decision, although extended support remains available until 2029, albeit potentially incurring additional costs for certain functionalities.
Vietbay delves into the intricacies of the divergence between Windows Server 2022 and its predecessor, shedding light on the novel features introduced in the latest iteration while also highlighting functionalities from Windows Server 2019 that have been retired.
Windows Server 2022 enhances over 2019
The Decision to Upgrade: A Strategic Perspective
Despite facing formidable competition, Windows Server continues to be a preferred choice among organizations. In response to the surging tide of cloud computing, Microsoft incorporated native Azure support in Windows Server 2019. Building upon this foundation, Windows Server 2022 enhances and extends the cloud computing capabilities, available across three editions. Microsoft offers support for upgrades from both Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019.
The pivotal question arises: is it worthwhile to transition from Windows Server 2019 to Windows Server 2022? To make an informed decision, one must explore the plethora of new features and improvements that the latest version brings to the table.
Exploring the Novel Features of Windows Server 2022
The salient features of Windows Server 2022 are categorized into three main pillars: security enhancements, Azure hybrid capabilities, and advancements in the application platform.
1. Security Enhancements
While Windows Server 2019 introduced Advanced Threat Protection, the relentless evolution of threats necessitated further fortification. Windows Server 2022 responds to this imperative by implementing key security features such as hardware root-of-trust, firmware protection, and virtualization-based security. At the core of its security architecture lies Secured-Core Server, safeguarding hardware, firmware, and the operating system against threats through the utilization of Trusted Platform Module 2.0 and Windows Defender System Guard. Notably, the Secure Message Block (SMB) network file sharing protocol is now encrypted by default, bolstering overall system security.
Additional security improvements include default activation of hypervisor-protected code integrity and the incorporation of Windows Defender Credential Guard for virtualization-based isolation, fortifying the protection of credentials and other sensitive assets traversing networks. Complementing these measures is a client capable of performing Domain Name System (DNS) lookups over Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS), mitigating potential interference with such crucial operations.
2. Azure Hybrid Capabilities
In terms of Azure integration, Windows Server 2022 introduces significant enhancements. The revamped SMB now employs the QUIC protocol, replacing the traditional Transport Control Protocol (TCP). This alteration facilitates seamless access to file servers hosted on Azure from any location—be it on-premises or within Azure—eliminating the need for a virtual private network (VPN). Azure Arc support is now integrated, facilitating the extension of on-premises and multi-cloud environments to Azure. The introduction of hotpatching allows updates to be installed on Windows Server virtual machines without necessitating a reboot.
3. Application Platform Advancements
Beyond securing SMB transmissions through encryption, Windows Server 2022 introduces data compression for enhanced performance. Furthermore, administrators can leverage the new browser-based Windows Admin Center for streamlined control over server infrastructure.
In conclusion, the decision to upgrade to Windows Server 2022 involves a comprehensive evaluation of its innovative features and improvements, weighing the potential benefits against the backdrop of organizational requirements and priorities. As technology continues to advance, embracing the latest server operating system becomes not merely a question of necessity but an opportunity to fortify security, enhance efficiency, and align with the evolving landscape of IT infrastructure.
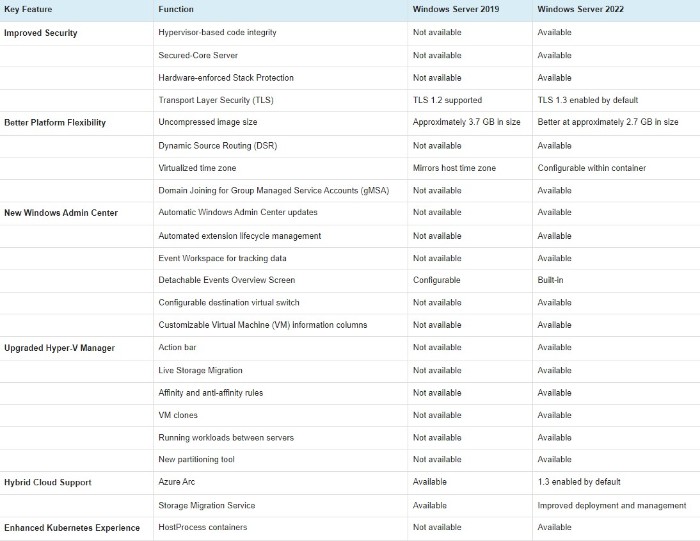
Key Feature Differences in Windows Server 2022 vs. 2019
To help determine the winner in a Windows Server 2022 vs. Windows Server 2019 showdown, you can look at the table below, which summarizes the major differences between the two versions.